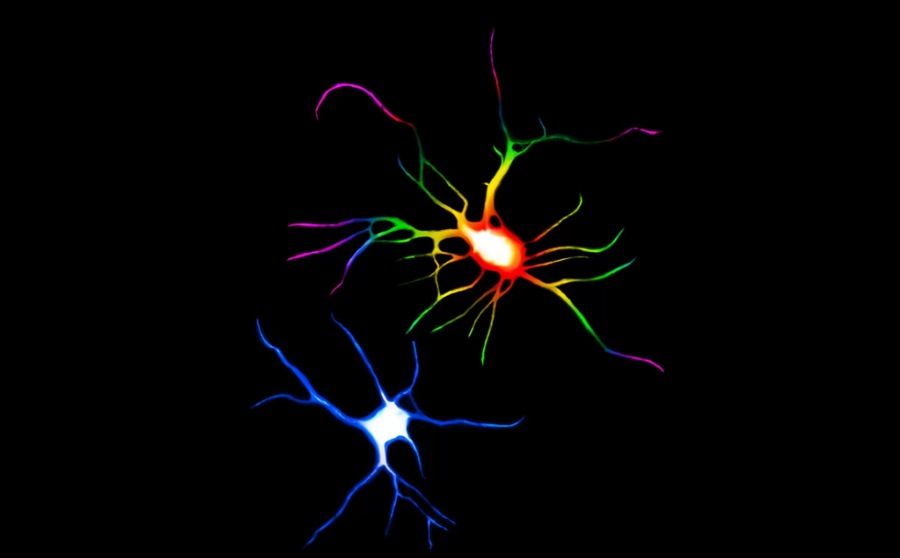
Psychedelics can change the structure of the brain and increase its capacity for repair
Psychedelic agents can alter the mind in a physical sense. Researchers have found that substances such as DMT and LSD alter brain structure in animals by increasing the ability of nerve cells to form new connections. As a result, psychedelics may help with depression, anxiety, addiction and post-traumatic stress disorder.
New research on psychedelics published this week on the „Cell Reports” show that these agents can positively affect mozg and play a major role in the treatment of diseasesob psychic. Researchers at the University of California, Davis, based their conclusions on their animal studies and comorks cultured in the laboratory.
Previous studies on psychedelics have already shown the positive effects of these agentsoin mozg. – People have long assumed that psychedelics are capable of altering neuronal structure, but this is the first study whichore clearly and unequivocally confirms this hypothesis – admitted David E. Olson, wspołautor of the publication. – Psychedelics are some of the most powerful compoundsoin whichoare known to affect the functioning of the mozgu. It is clear to me that we need to understand how they work – Olson added.
The concept that these substances can pomoc in the fight against mental disorders such as depression, for example, is also not new. Neurites in prefrontal cortex during prolonged depression, may regress and shrink. Psychedelics can reverseocate this process, opening an important new avenue for finding effective treatments.
– One of the hallmarks of depression is that neurites in the prefrontal cortex – a key area of the mozgu, ktory regulates emotions, nastroj and anxiety – tend to shrink – added the researcher. But similar changes in mozgu also affect the state ofoin anxiety, addiction or post-traumatic stress disorder.
Rats, fruit fliesowki and the freshwater fish danio striped bass received small doses of the agents during experimentsoin psychedelics. These substances induced a neurite increase in themow, bridgingoin between neurons, whichore enable internal communication. Psychedelics also increased dendrite densityow and synapses. These structures play an important role in communication channels mozgu.
The researchers admittedly did not conduct any experimentsoin humans, but experiments conducted on vertebrates and invertebrates showed that psychedelics produced similar effects in rotional speciesow. This indicates that biological mechanisms thatore respond to psychedelics remained the same, suggesting that psychedelics are likely to have the same effect in humans.
Syndromeoł Olsen now wants to investigate whether these psychedelic agents can be used to improve plasticity mozgu – its ability to repair itself – without associated hallucinations or other side effects. This will require further investigation into how toob these substances affect mozg, and in particularolibilities, whichore biological pathways activate and what proteins produce.
– Our work shows that there are many distinct chemicals capable of promoting plasticity mozgu, such as ketamine – explained Olson, while also adding that finding them can pomoc in developing safe and effective alternatives to.
Sourceobackground: Science Daily, Live Science, fot. Calvin and Joanne Ly/ CC BY-ND